
Nutritional Therapy
This Topic Covers:
Therapy
treatment with food sources...food as medicine. Clinical nutrition explained.
Overview of organic food and why organic may be better. A-Z guide of vitamin and
mineral content of food intake. Listings of power and functional foods, and more...
(Nutrition
Explained)
What Is Clinical
Nutrition
What Are Whole Foods
Nutrient Density of Foods
Look Up Nutrient Density of Food Index Guide
Power and Functional Foods
Finding Help -
Nutritionists vs. Dietitians
Benefits of
Consulting a Nutritionist
Find a Certified
Clinical Nutritionist
What Is a
Holistic Nutrition Consultant
Raw Food Therapy
Understanding
Organic Labels, Benefits and Claims
Organic Better
Nutrition
Reasons You
Should Buy Organic
What Does Organic
Mean (Organic Standards)
Shopper's Guide
to Pesticides in Produce
Personalized
Nutrition
Dietary and
Vitamin Supplementation
Professional &
Physician Grade Supplements
Which Name Brands
Are Gold Standard Supplements
Nutritional
Treatment Therapy Applications
Nutrient Content
of Food Resources
Listings of Power
Foods
Nutritional
Journals
Nutritional
Associations
Spiritual Nutrition
 Introduction
Dr. Linus Pauling, winner
of two Nobel Prizes stated: “You can trace every sickness, every disease and
every ailment to a mineral deficiency.” Introduction
Dr. Linus Pauling, winner
of two Nobel Prizes stated: “You can trace every sickness, every disease and
every ailment to a mineral deficiency.”
Retrieved from - www.bloodindex.org
Diet
and Nutrition form the basic foundation for health and its development. Good
nutrition means stronger immune systems, less illness and better health! Healthy
people are stronger, are more productive in their day-to-day activities.
Diet
and Nutrition plays a vital role in the maintenance of good health and in the
prevention and cure of disease. The right kind of food is the most important
single factor in the promotion of health; and the wrong does the opposite
effect.
The human body builds and maintains healthy cells, tissues, glands and organs
only with the help of nutrients. The food which provides these nutrients is thus
one of the most essential factors in building and maintaining health.
The
primary cause of disease is a weakened organism or lowered resistance in the
body because of nutritional deficiency.
It's assumed that 45 chemical components and elements are needed by human cells
including oxygen and water. Others are classified into five main groups, namely
carbohydrates, fats, proteins, minerals and vitamins. All nutrients are vitally
important and they work together and the absence of any of them will result in
disease.
top
 Alarming Health Statistics Alarming Health Statistics
Reference - www.who.int
- World Health Organization
Call to action: There is now a large, convincing body
of evidence that dietary patterns and the level of physical activity can not
only influence existing health levels, but also determine whether an
individual will develop chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular
disease and diabetes.
These chronic diseases remain
the main causes of premature death and disability in industrialized
countries and in most developing countries. Developing countries are
demonstrably increasingly at risk, as are the poorer populations of
industrialized countries.
In communities, districts and countries where
widespread, integrated interventions have been implemented, dramatic
decreases in risk factors have occurred. Successes have come about where the
public has acknowledged that the unnecessary premature deaths that occur in
their community are largely preventable and have empowered themselves and
their civic representatives to create health-supporting environments. This
has been achieved most successfully by establishing a working relationship
between communities and governments; through enabling legislation and local
initiatives affecting schools and the workplace; by involving consumers’
associations; and by involving food producers and the food-processing
industry…
There is a need, on a
continuing basis, to develop strategies to change people’s behavior towards
adopting healthy diets and lifestyles, including research on the supply and
demand side related to this changing consumer behavior…
Beyond the rhetoric, this epidemic can be halted -
the demand for action must come from those affected. The solution is in our
hands.
Making the best of
health services and the professionals who provide them:
The training of all health professionals (including physicians,
nurses, dentists and nutritionists) should include
diet, nutrition and physical activity as key determinants of medical and dental
health. The social, economic, cultural and psychological determinants of
dietary and physical activity choice should be included as integral elements of
public health action.
There is an urgent
need to develop and strengthen existing training programmes to implement these
actions successfully.
top
 What is Clinical Nutrition What is Clinical Nutrition
Reference
-
www.umm.edu
-
The University of Maryland School of Medicine
What
is clinical nutrition?
Clinical nutrition is the study of the relationship between food and the
well-being of the body. More specifically, it is the science of nutrients and
how they are digested, absorbed, transported, metabolized, stored, and
discharged by the body. Besides studying how food works in the body,
nutritionists are interested in how the environment affects the quality and
safety of foods, and how these factors influence health and disease.
What
is the history of clinical nutrition?
The study of human nutrition dates back to the 18th century, when the French
chemist Lavoisier discovered that there was a relationship between our
metabolism of food and the process of breathing. By the early 20th
century, scientists had found that diseases were associated with certain diets (beri-beri,
rickets, scurvy and pellagra). Later it was found that these diets lacked
specific nutrients (namely vitamin B1 (thiamine), vitamin D, vitamin C, and
vitamin B3 (niacin) respectively). By 1912, the Polish chemist Casimir Funk had
found a substance (vitamin B1) that actually prevented beri-beri, and he named
it "vitamine."
In
the early 1940s, Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) were established by the
National Research Council. The RDAs define the minimal nutrient intakes
necessary for the prevention of basic deficiency diseases like beri-beri and
rickets. Until recently, these guidelines were used to set nutritional adequacy
standards for the general population.
Researchers
and scientists also continue to uncover the therapeutic role of individual
nutrients in the prevention and treatment of disease. For example,
antioxidants like
beta-carotene, selenium, vitamin E, and vitamin C, particularly from foods,
appear to protect against the development of heart disease, cancer, and other
chronic degenerative diseases.
Dietary
Reference Intakes (DRI’s) have been developed to show how much of a
nutrient we need every day to maximize health and lower the risk of chronic
disease (in contrast to RDAs which state the minimal amount to avoid disease
secondary to deficiencies).
The field of clinical nutrition has evolved into a practice that is increasingly
incorporated into mainstream medical treatment.
What
constitutes a healthful diet?
The optimal diet for improving health has to be individualized to meet
your unique needs. The USDA food pyramid suggests that we use fat "sparingly,"
and that our daily diet include two to three servings of dairy products; two to
three servings of meat, poultry, fish, eggs, beans, or nuts; three to five
servings of vegetables; two to four servings of fruit; and six to eleven
servings of bread, cereal, rice, or pasta. But the numbers alone don't tell the
whole story.
Our food
needs are influenced by many factors, including age, gender, body size,
pregnancy, and health.
A clinical nutritionist can help you determine what type of diet is best for
you.
What
are nutritional supplements?
The term "nutritional supplement" refers to vitamins,
minerals, and other food components that are used to support good health and
treat illness. For example, plant compounds known as phytochemicals (found
abundantly in tomatoes and soybeans, for example) have powerful disease-battling
properties.
While it's possible almost all of the time to successfully
incorporate nutrients into your diet alone, supplementation can help maintain
sufficient levels and produce specific desired effects. For example,
supplementation with zinc supplementation has been shown to reduce the duration
of the common cold and decrease the incidence of acute diarrhea in
children.
top
 What is
Meant by
"Whole Foods"? What is
Meant by
"Whole Foods"?
Reference
-
www.whfoods.org
Whole foods contain nothing more than
the naturally occurring nutrients and phytonutrients intrinsic to the original
plant or animal from which the food was derived. Whole foods rely on the natural
components for their delicious flavors, vibrant colors, and rich textures. Whole
foods retain all their vital constituents in the original form in which Nature
provided to them; no nutrients have been removed or remodeled, and no synthetic,
artificial chemicals have been added.
What are Essential Nutrients and Why are They Important?
Essential nutrients are nutrients that your body can't make on its own,
therefore, you must get these important molecules from the food you eat.
Essential nutrients classically include vitamins and minerals, as well as some
amino acids and specific fatty acids. Whole foods are a preferred choice for
these important nutrients since whole foods contain a range of different
molecules, and often have these nutrients at the highest levels. In addition,
whole foods have these nutrients in their natural, unchanged state. Often during
processing, these nutrients are either destroyed or can be changed to other
non-nutritious compounds. For example, when oils are exposed to high heat during
processing or cooking, not only is their natural complement of anti-oxidants
used up, but free radicals and trans-fats may be formed. The result is a food
that no longer promotes health.
top
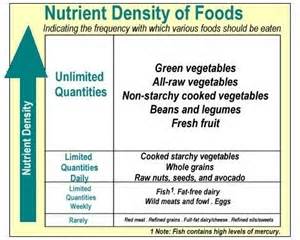 Nutrient Density of
Foods Nutrient Density of
Foods
Reference -
www.whfoods.com
Like anything involving "density," "nutrient density"
means how much you get of one thing, given the presence of something else.
In the case of nutrient density, the "things" you receive, the nutrients,
are analyzed in relationship to how much they "cost" you, in terms of
calories. Simply stated, nutrient density means how many nutrients you get
from a food, given the number of calories it contains. Nutrient density is a
simple way to connect nutrients with calories.
Nutrient dense foods give you the most nutrients for
the fewest amount of calories. In other words, nutrient dense foods give you
the "biggest bang for the buck." You get lots of nutrients, and it doesn't
cost you much in terms of calories...
No foods are more nutrient dense than
whole, organically-grown foods. The reason is simple: nothing is contained
in a fresh, whole organic food that doesn't need to be there.
Retrieved from -
www.drfuhrman.com
Nutrient Density is
a critical concept in devising and recommending dietary and nutritional
advice to patients and to the public. Not merely vitamins and minerals, but
adequate consumption of phytochemicals is essential for proper functioning
of the immune system and to enable our body’s detoxification and cellular
repair mechanisms that protect us from chronic diseases.
Nutritional science in the last twenty years has
demonstrated that colorful plant foods contain a huge assortment of
protective compounds, most of which still remain unnamed. Only by eating an
assortment of nutrient-rich natural foods can we access these protective
compounds and prevent the common diseases that afflict Americans. Our
modern, low-nutrient eating style has led to an overweight population, the
majority of whom develop diseases of nutritional ignorance, causing our
medical costs to spiral out of control.
Nutrient Density Index Guide
www.wholefoodsmarket.com
ANDI stands for "Aggregate Nutrient Density Index." An
ANDI score shows the nutrient density of a food on a scale from 1 to 1000
based on nutrient content. ANDI scores are calculated by evaluating an
extensive range of micronutrients, including vitamins, minerals,
phytochemicals and antioxidant capacities.
tv.greenmedinfo.com
Dr. Joel Fuhrman breaks down the highest nutrient per
calorie foods. He provides a list of the most nutrient dense foods that we
should all be aware of.
ndb.nal.usda.gov
National Nutrient
Database for Standard Reference - Find nutrient
information on over 8,000 foods using this new and improved search feature.
You can now search by food item, group, or list to find the nutrient
information for your food items. In addition, you can now access the USDA
Ground Beef Calculator from the same search page.
Start your search here.
top
 Functional Power Foods Functional Power Foods
“Functional Foods” are foods or dietary components that may provide a health
benefit beyond basic nutrition.
You can take greater control of your health through the food choices you
make, knowing that some foods can provide specific health benefits. Examples
can include fruits and vegetables, whole grains, fortified or enhanced foods
and beverages, and some dietary supplements.
Reference -
www.foodinsight.org
Many academic, scientific and regulatory bodies have developed, or are
developing, guidelines to establish the scientific evidence base needed to
support and further validate claims for functional components or the foods
containing them. FDA regulates food products according to their intended use
and the nature of claims made on the package. Five types of health-related
statements or claims are allowed on food and dietary supplement labels:
-
Nutrient content claims
indicate the presence of a specific nutrient at a certain level.
-
Structure and function claims
describe the effect of dietary components on the normal structure or
function of the body.
-
Dietary guidance claims
describe the health benefits of broad categories of foods or diets and
do not refer to a disease or a health related condition.
-
Qualified health claims
convey a developing relationship between components in the diet and
reduced risk of disease, as reviewed by the FDA and supported by the
weight of credible scientific evidence available.
-
Health claims confirm a relationship between components in the diet and
reduced risk of disease or health condition, as approved by FDA and
supported by significant scientific agreement.
The scientific community continues to increase its understanding of the
potential for functional foods and their role in maintaining and optimizing
health. For benefits to be validated and claims to be made, a strong
and reliable body of credible scientific research is needed to confirm the
benefits of any particular food or component. For functional foods to
deliver their potential public health benefits, consumers must be able to
rely on the scientific criteria that are used to document such health
statements and claims.
Link
to
Power Food Section
for
More
Detail
top
 Finding Help
- Nutritionists vs. Dietitians
Finding Help
- Nutritionists vs. Dietitians
holisticprimarycare.net - Copyright @ Holistic Primary Care. All
Rights Reserved
Surrounded by a food environment that is arguably more bountiful and less
nutritious than ever before, many Americans have a pressing need for access
to high-quality nutrition information and nutrition-focused health care
practitioners. But like so many other aspects of health care in this
country, meeting this seemingly simple need is fraught with complications.
Almost as extensive as the assortment of foodstuffs available to American
consumers is the variety of nutrition service providers. Diverse
professionals with varying titles and credentials now vie with each other to
offer some form of nutrition counseling or food-based therapy to the
health-conscious public.
As the nutrition service professions continue to grow and diversify, it is
imperative that those in search of diet-related guidance understand how to
navigate the broad and varied network of nutrition providers.
This can be a challenge not only for patients but for physicians as well:
How do you find well-qualified, credible nutrition professionals to whom you
can confidently refer patients when their specific needs exceed your own
nutritional knowledge?
On one end of the nutrition services spectrum is the profession of
dietetics. The
Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, formerly
known as the American Dietetic Association, defines the profession as the
"integration, application and communication of principles derived from food,
nutrition, social, business and basic sciences, to achieve and maintain
optimal nutrition status of individuals through the development, provision
and management of effective food and nutrition services in a variety of
settings."
Another branch of nutritional medicine that has emerged in recent years is
the field of Clinical Nutrition. Similar to RDs, Certified Clinical
Nutritionists (CCNs) also, at a minimum, hold a BS degree, have completed a
supervised internship, and passed a national board certification
examination...Based on the concepts of biochemical individuality and
person-centered care, Clinical Nutrition is part of a larger nutrition
specialty that may be broadly defined as Holistic Nutrition.
top
 Benefits of Consulting
a Registered Dietitian
Benefits of Consulting
a Registered Dietitian
www.eatright.org - Copyright © | Academy of Nutrition and
Dietetics, All Rights Reserved
Top Ten
Reasons Why Consulting with a Registered Dietitian Can Benefit You
The Find a Registered Dietitian online referral
service allows you to search a national database of qualified food and
nutrition practitioners -
Find a registered dietitian near you »
Reference - www.iaacn.org
To Find a Clinical Nutritionist in your area - email: dc@clinicalnutrition.com
top
What
Is a Holistic Nutrition Consultant
www.holisticprimarycare.net
- Copyright @ Holistic Primary Care. All Rights Reserved
Contemporary applications of the ancient concept of
food-as-medicine are evident in the growing fields of holistic nutrition
counseling and nutrition coaching. Regardless of their specific titles,
holistic nutrition providers across all disciplines share the common goal of
offering individualized, whole-person care that addresses the complete and
unique nutritional needs of their patients. They tend to encourage diets
based on whole foods and emphasize elements of food quality, seasonality,
and sustainability--aspects that are often missing from the more
institutional practice of dietetics.
top
 Raw Food Therapy Raw Food Therapy
Reference Source -
www.rawfoodlife.com -
© Copyright
The Science of Raw Food:
A raw food diet is not just good for you - it’s also good science!…Basically,
raw food (sometimes called live or living food) is food that has not been
cooked or exposed to temperatures over 118°F.
At that temperature, the natural enzymes in food are completely destroyed.
Enzymes are essential for all the chemical processes in your body,
especially digestion. In addition, nutrients are chemicals, and when these
chemicals are heated it causes chemical reactions – just like in your high
school chemistry class - the higher the heat, the more volatile, or
destructive, the chemical reactions.
Scores of unnatural chemical by-products with damaging effects on
health are produced by cooking. For example, cooked carbohydrates can do
much more than create weight problems. They can turn into a carcinogen
called acrylamide, a chemical used to make plastics and dyes that have
caused cancer in animals - the higher the cooking temperature, the greater
the levels of acrylamide. Frying, one of the worst kinds of cooking makes
oils oxidize creating harmful ‘free radicals’ and increasing the risk of
cancer, heart disease and premature aging. Ironically, frying also destroys
the Vitamins A and E which we need to protect us from free radicals.
therawfoodinstitute.com
- © The Raw Food Institute
When you cook food, you lose at least 30% of the
nutrients and 100% of the enzymes in that food. Nutrients are the building
blocks of cells in our bodies and enzymes aid digestion and other bodily
functions. Further, cooking food chemically changes the molecular structure
of raw plants which may convert to toxins, carcinogens, mutagens and
free-radicals associated with diseases like diabetes, arthritis, heart
disease and cancer. You could almost call them ‘healing food’.
Having a good balance of raw foods in your diet helps
reduce these toxic risks by flooding your body with the most nutritious food
possible, giving your body the ability to heal and rejuvenate at a deep
cellular level.
One of the most important aspects of raw food is
enzymes. Enzymes are the building blocks of life! Our bodies’ enzymes are
responsible for every single action in our body: from chewing and digesting
our food, to waking up in the morning and brushing our teeth. Your body
produces some of its own enzymes, but you also need help from your food.
If you don’t have enough enzymes, your body won’t have
the energy to develop new cells, fight off infections, or digest your food.
By feeding your body raw foods, your body is literally being fed energy!
When your body has help from foods’ enzymes, you’ll have more energy than
ever imagined! This extra energy can be used to heal your body and help
create the vibrant life you’ve always wanted.
Raw foods also help your body reach an alkalized
state—where healing, weight loss, and detoxification occur.
There are two types of foods: acidic and alkaline.
Acidity encourages decomposition, decay, disease and energy loss. Alkaline
foods support detoxification and balance in the body. Our natural body
creates both acidity and alkalinity, but the typical American diet overloads
our system with too much acidity. Foods like sugar, meat, alcohol, cheese,
and chocolate are very acidic and damaging during the cleansing and healing
process.
With the powerful benefits from enzymes and the
detoxification of alkalizing foods, raw food allows for:
-
Increased energy
-
Better digestion
-
Weight loss
-
Reduced risk of heart disease
-
Reduced risk of diabetes and cancer
-
A great sense of wellbeing
-
Improved skin appearance
-
Connection to your food and surroundings
-
A highly ethical and sustainable diet
…Detoxifying improves health,
energy, immune system, memory and digestion. Detoxifying with special
cleansing diets, like raw food, is the best way to assist your body in the
elimination process. The Raw Food Institute's cleansing process is most
important for those suffering from immune-related diseases like cancer,
arthritis, diabetes, chronic fatigue, heart disease, and much more. Many
illnesses are caused by the constant presence of unwanted buildup toxic
substances. By cleansing, you’re ridding your body of dead, harmful waste
and rejuvenating it with pure energy.
But cleansing and eliminating doesn’t just mean not
consuming toxins. You need to actively flush out your system by consuming
nutritious, medicinal food that helps eliminate waste.
www.prevention.com
- Reports,
Pros And Cons Of The Raw Food Diet
...Raw Food’s Technical
Difficulty: While the theory behind raw foods is plausible in many
respects, it runs contrary to traditional Chinese and Ayurvedic teachings.
These ancient health systems assert that nutrients from cooked food are more
digestible because the cooking process breaks them down into smaller
components, thereby supporting our “digestive fire.” This term is not
referring to the type of "digestive fire" we typically associate with heart
burn, for example, but to a warmth and movement that brings vitality to the
digestive tract and maintains our overall health…
Cooked Food Is Nutritious:
Some nutrients become more bioavailable once they are heated. Lycopene, for
example, an antioxidant found in tomatoes
and other foods, is shown to be more nutritionally available when
cooked. Vegetables such as kale, spinach, onions, and garlic are also shown
to be more nutritious when cooked because light cooking releases compounds
that might otherwise go undigested. Of course, overcooking foods,
particularly meats, produces acrylamide and other chemicals that contribute
to inflammation and cancer. So, as always, balance
is in order. For optimal results, I recommend light steaming or
sautéing at moderate temperatures. This will help make nutrients more
available and easier to absorb, without producing harmful by-products of
overcooking.
Balance Is the Only Real
Answer: There are numerous well-documented benefits
to eating large amounts of fresh produce. But my advice is to strive for a
well-rounded diet that incorporates raw and lightly cooked foods, raw
healthy fats, lean protein, complex carbohydrates, and organic fruits and
vegetables. This balanced approach will go a long way toward providing you
the nutrients you need to maintain overall health, clarity, and vitality
naturally.
The Bottom Line: No single diet offers a
magical formula for vibrant health. In fact, no single diet works for
everyone. While raw foods may not be ideal for people with weak digestion,
such a diet can offer significant results for others. As a holistic
practitioner, I believe that a 100 percent raw food diet is not the best
choice for everyone. Over time, a 100 percent raw food approach can place
undue stress on the digestive system and cause weakness in certain people.
While the abundance of fresh produce is no doubt beneficial, most of us need
some balance between cooked and raw foods for optimal vitality over the long
term.
Copyright ©2014 Rodale Inc. "Prevention" and "Prevention.com"
top
Understanding
Organic Food Labels, Benefits and Claims
www.helpguide.org -
‘©Helpguide.org. All rights reserved.
Helpguide.org is an ad-free non-profit resource for supporting better mental
health and lifestyle choices for adults and children.’
Organic food has become very popular. But navigating
the maze of organic food labels, benefits, and claims can be confusing. Is
organic food really healthier? Is it more nutritious? What do all the labels
mean? Why is it so expensive? This guide can help you make better choices
about which organic foods are healthier for you and better for the
environment, and how you can afford to incorporate more organic food into
your diet.
Read
more...
top
 Organic Better Nutrition Organic Better Nutrition
Reference Source -
www.organicconsumers.org
BOULDER, Colo. - March 19, 2008 /Natural Newswire/ - A comprehensive review
of 97 published studies comparing the nutritional quality of organic and
conventional foods shows that organic plant-based foods (fruits, vegetables,
grains) contain higher levels of eight of 11 nutrients studied, including
significantly greater concentrations of the health-promoting polyphenols and
antioxidants.
In this first comprehensive review of the scientific literature comparing
nutrient levels in organic and conventional food completed since 2003, a
team of scientists conclude that organically grown plant-based foods are 25%
more nutrient dense, on average, and hence deliver more essential nutrients
per serving or calorie consumed...Read
more...
Reference -
www.ota.com
- © Organic Trade Association
Organic
foods are rich in nutrients:
Growing crops in healthy soils results
in food products that offer healthy nutrients. There is mounting evidence that
organically grown fruits, vegetables and grains may offer more of some
nutrients, including vitamin C, iron, magnesium and phosphorus, and less
exposure to nitrates and pesticide residues than their counterparts grown using
synthetic pesticides and fertilizers….
Soil Health:
Organic
producers also must follow a National List of Acceptable and Prohibited
Materials concerning pest control treatments, fertilizers and seed treatments
that they use. All agricultural materials must be evaluated for their long-term
effects on the environment and not simply whether they are synthetic or
natural…
Alternative to
Genetic Engineering:
Because
U.S. national organic standards and industry practices do not allow the use of
genetic engineering in the production and processing of organic products,
organic agriculture gives consumers who wish to avoid genetically modified foods
a choice in the marketplace…
Although
genetic engineering (GE) proponents claim GE crops will cut pesticide use, this
is not necessarily true. On the other hand, organic agriculture does reduce such
exposure because it avoids the use of toxic and persistent pesticides…
The Global
Environment: There is
growing evidence of the beneficial effects of organic practices on the global
environment:
Research
at the Rodale Institute has shown that organic practices can remove about 7,000
pounds of carbon dioxide from the air each year and sequester it in an acre of
farmland…
Research
shows a difference in children who eat organic:
The findings from this study demonstrate that dietary intake of OP
pesticides represents the major source of exposure in young children.”…
Fertilizers and the
Health of Aquatic Systems:
Because organic agriculture respects the balance of microorganisms in the
soil, organic producers use composted manure and other natural materials, as
well as crop rotation, to help improve soil fertility, rather than
petroleum-based synthetic fertilizers that can result in an overabundance of
nitrogen and phosphorous in the ground. As a result, organic practices help
protect ground water supplies and avoid runoff of chemicals that can cause
"dead zones" in larger bodies of water…
Antibiotics in Agriculture:
Organic practices prohibit the use of hormones, antibiotics or other animal
drugs in animal feed for the purpose of stimulating the growth or production of
livestock… Thus, organic practices avoid the abuse of antibiotics that could
have profound consequences for treatment of disease in humans, including the
serious dangers of antibiotic-resistant bacteria…
Protecting the Next Generation:
Organic
agriculture minimizes children’s exposure to toxic and persistent pesticides
in the soil in which they play, the air they breathe, the water they drink, and
the foods they eat. A
recent study of 600 people found that those exposed to pesticides had a 1.6
times greater risk of developing Parkinson’s disease than those who were
not….
Reference -
whfoods.org
- © The George Mateljan Foundation, All Rights Reserved
Can organic foods really improve my health? Yes. Organically grown food is your best way of reducing
exposure to toxins used in conventional agricultural practices. These toxins
include not only pesticides, many of which have been federally classified as
potential cancer-causing agents, but also heavy metals such as lead and mercury,
and solvents like benzene and toluene. Minimizing exposure to these toxins
is of major benefit to your health. Heavy metals damage nerve function,
contributing to diseases such as multiple sclerosis and lowering IQ, and also
block hemoglobin production, causing anemia. Solvents damage white cells,
lowering the immune system's ability to resist infections. In addition to
significantly lessening your exposure to these health-robbing substances,
organically grown foods have been shown to contain substantially higher levels
of nutrients such as protein, vitamin C and many minerals.
Are organic foods nutritionally superior to
conventionally grown foods? Yes, and significantly more. Proof of their superiority has
been demonstrated in numerous studies. In 1998, a review of 34 studies comparing
the nutritional content of organic versus non-organic food was published in the
peer-reviewed, MEDLINE-indexed journal Alternative Therapies (Volume 4, No. 1,
pgs. 58-69). In this review, organic food was found to have higher protein
quality in all comparisons, higher levels of vitamin C in 58% of all studies,
5-20% higher mineral levels for all but two minerals. In some cases, the mineral
levels were dramatically higher in organically-grown foods-as much as three
times higher in one study involving iron content.
A review of 41 studies comparing the nutritional value of
organically to conventionally grown fruits, vegetables and grains, also
indicates organic crops provide substantially more of several nutrients,
including:
-
27% more vitamin C
-
21.1% more iron
-
29.3% more magnesium
-
13.6% more phosphorus
The review also found that while 5 servings of organically
grown vegetables (lettuce, spinach, carrots, potatoes and cabbage) provided the
daily recommended intake of vitamin C for men and women, their conventionally
grown counterparts did not. Plus, organically grown foods contained 15.1% less
nitrates than conventionally grown foods. Nitrates, a major constituent of
chemical fertilizers, bind to hemoglobin and, particularly in infants, can
significantly reduce the body's ability to carry oxygen…
What substances do we avoid by eating organic food?
Over
3,000 high-risk toxins routinely present in the U.S. food supply are, by law,
excluded from organic food, including:
Pesticides: By far the largest group of toxins to be
largely prohibited from organically grown foods are synthetic pesticides, which
are found virtually everywhere else in the food supply. Several hundred
different chemicals and several thousand brand-name pesticide products are
legally used in commercial food production in the U.S. Act of 1992; the
Environmental Protection Agency had classified 73 pesticides authorized for
agricultural use as potential carcinogens (cancer-causing agents). And
pesticides don't just remain where they are applied. A 1996 study by the
Environmental Working Group found 96% of all water samples taken from 748 towns
across the U.S. contained the pesticide atrazine, and at least 20 different
chemical pesticides are routinely present in municipal tap water across the U.S.
Heavy metals: The toxic metals cadmium, lead, and
mercury enter the food supply through industrial pollution of soil and
groundwater and through machinery used in food processing and packaging.
Cadmium, which can be concentrated in plant tissues at levels higher than those
in soil, has been linked to lung, prostate and testicular cancers. Despite
lead's long-recognized serious adverse impact on health, especially that of
young children, lead solder is still used to seal tin cans, imparting the lead
residues found in many canned foods. Even low levels of lead are harmful and are
associated with decreased intelligence, impaired neurobehavioral development,
decreased stature and growth, and impaired hearing. Mercury is toxic to brain
cells and has been linked to autism and Alzheimer's disease.
Solvents: Used to dissolve food components and
produce food additives, solvents are also virtually omnipresent in commercially
processed food. Solvents, such as benzene and toluene have been linked to
numerous cancers. Benzene, specifically, has been repeatedly associated with
rheumatoid arthritis-an auto-immune condition involving pain and degeneration in
the joints that affects over 2 million adults in the U.S.
Not only are these toxic substances harmful singly, but
when combined, as they are in commercially grown and processed food, and in the
human body where they accumulate, their effects have been found to be magnified
as much as a 1,000-fold.
top
 Reasons
to Go Organic Reasons
to Go Organic
Reference Source -
www.organicconsumers.org
Organic Food is Pure Food, Free of
Chemical Additives - Organic Food is Safer
-
Organic food doesn't contain pesticides. More than 400 chemical pesticides
are routinely used in conventional farming and residues remain
on non-organic food even after washing. Children are
especially vulnerable to pesticide exposure. One class of pesticides, endocrine
disruptors, may be responsible for early puberty and breast
cancer. Pesticides are linked to asthma
and cancer.
-
Organic food isn't genetically modified. Under organic
standards, genetically modified (GM) crops and ingredients are
prohibited.
-
Organic animals aren't given drugs.
Organic farming standards prohibit the use of
antibiotics, growth hormones and genetically modified
vaccines in farm animals.
Hormone-laced
beef and dairy consumption is correlated with increased rates
of breast, testis and prostate cancers.
-
Organic animals aren't
fed slaughterhouse waste, blood, or manure.
Eating organic reduces the risks of CJD,
the human version of mad
cow disease, as well as
Alzheimer's.
-
Organic animals aren't fed arsenic.
-
Organic animals aren't fed byproducts
of corn ethanol production (which increases the rate of E.
coli contamination).
-
Organic crops aren't fertilized with toxic sewage sludge or coal
waste, or irrigated with E. coli contaminated sewage
water.
-
Organic food isn't irradiated. Cats fed a diet of irradiated
food got multiple
sclerosis within 3-4 months.
-
Organic food contains less
illness-inducing bacteria. Organic
chicken is free of salmonella and has a reduced incidence of
campylobacter.
-
Organic dairy has environmental
benefits: Shades
of Green: Quantifying the Benefits of Organic Dairy Production
-
Organic food doesn't contain food
additives, flavor enhancers (like MSG),
artificial sweeteners (like
aspartame and high-fructose
corn syrup), contaminants (like
mercury)
or preservatives (like sodium
nitrate), that can cause health problems.
-
Eating organic has the potential to lower
the incidence of autism, learning
disorders,
diabetes, cancer,
coronary heart
disease, allergies, osteoporosis,
dementia,
and hyperactivity.
top
 Organic Standards Organic Standards
What do the food labels such as “organic,” "natural,"
"free-range," and "non-GMO" really mean? Understanding this terminology is
essential when you’re shopping for organic foods.
The most important point to
remember is that "natural" does not equal organic. "Natural" is an
unregulated term that can be applied by anyone, whereas organic
certification means that set production standards have been met. These
production standards vary from country to country—in the U.S., for example,
only the "USDA Organic" label indicates that a food is certified organic.
Similar certification labels are also offered on organic products in other
parts of the world, including the European Union, Canada, and Australia.
USDA Certified Organic Food Labels in the U.S.- When
you’re shopping for organic foods in the U.S., look for the “USDA Organic”
seal. Only foods that are 95 to 100 percent organic can use the USDA Organic
label.
Reference -
www.ams.usda.gov 
The organic standards describe the specific
requirements that must be verified by a USDA-accredited certifying agent
before products can be labeled USDA organic. Overall, organic operations
must demonstrate that they are protecting natural resources, conserving
biodiversity, and using only approved substances. A brief summary is
provided below:
Organic crops. The
USDA organic seal verifies that irradiation, sewage sludge, synthetic
fertilizers, prohibited pesticides, and genetically modified organisms were
not used.
Organic livestock. The
USDA organic seal verifies that producers met animal health and welfare
standards, did not use antibiotics or growth hormones, used 100% organic
feed, and provided animals with access to the outdoors.
Organic multi-ingredient foods. The
USDA organic seal verifies that the product has 95% or more certified
organic content. If the label claims that it was made with specified organic
ingredients, you can be sure that those specific ingredients are certified
organic.
top
Shopper's Guide to
Pesticides in Produce
Reference –
www.ewg.org (Environmental Working Group)
The Shopper's Guide to
Pesticides in Produce™
will help you determine
which fruits and vegetables have the most pesticide residues and are the
most important to buy organic. You can lower your pesticide intake by
avoiding the 12 most contaminated fruits and vegetables and choosing the
least contaminated produce.
top
 Personalized Nutrition Personalized Nutrition
Reference Source -
www.foodinsight.org
© Institute of Food Technologists
According to experts at the Institute of Food Technologists (IFT) Annual
Meeting & Food Expo®, personalized nutrition that optimizes health based on
an individual's phenotype (genetics, diet, lifestyle and environment) is the
future of diet and food.
The science of nutrigenomics – which looks at the effects of an individual's
phenotype on their overall health – is gaining momentum, and within 10
years, should revolutionize the way food is made, marketed and consumed.
As scientific and technological advances develop in the
field of health and nutrition, more and more focus has been directed toward
the emerging field of nutrigenomics or “personalized nutrition.” The science
of nutrigenomics involves the application of the human genome to nutrition
and personal health to provide individual dietary recommendations. By using
an individual’s unique genetic makeup and nutritional requirements to tailor
recommendations, consumers may one day have a greater ability to reduce
their risk of disease.
Personalizing nutrition to an individual’s unique
genetic makeup has the potential for positive health outcomes overall.
Choosing an individualized approach, over a more traditional or general
approach, to health and nutrition recommendations can provide consumers with
the most appropriate and beneficial information for their specific
nutritional needs. While personalized nutrition seems promising, research is
still in the preliminary stages, and years may pass before accurate and
effective recommendations can be made for individuals.
Reference -
www.futuremedicine.com
Diet and genomes interact. Nutrition has the most important life-long
environmental impact on human health. While nutrigenetics addresses how an
individual’s genetic makeup predisposes for dietary susceptibility,
nutrigenomics asks how nutrition influences the expression of the genome.
Nutrigenomics builds on the three omics disciplines transcriptomics,
proteomics and metabolomics. They are a prerequisite for nutritional systems
biology, the understanding of the interaction between food components and
diet with cells, organs and the whole body.
Personalized nutrition is a
conceptual analog to personalized medicine. While there are food products
available that address requirements or preferences of specific consumer
groups, these products are based on empirical consumer science rather than
on nutrigenomics and nutrigenetics. The latter two build the science
foundation for understanding human variability in preferences, requirements
and responses to diet, and may become the future tools for consumer
assessment motivated by personalized nutritional counseling for health
maintenance and disease prevention.
www.signaturesupplements.com
Science and the Wisdom of Nature Can Match Your Nutrition To Your
Unique Biochemistry: Over the
last 20 years
Signature Supplements'™
team of doctors,
scientists and nutritionists have been expanding the original discoveries of Dr.
Carl Pfeiffer, Dr. William Walsh, and Dr. Roger Williams who pioneered the
innovative field of individualized nutrition. Now we are able to identify
your individualized nutritional BioType™ and match it with a specific
nutritional program of supplements and foods that are determined by assessing
the needs of your uniquely inherent biochemistry.
Completing our
clinically developed questionnaire, allows our doctors to determine whether your
expressed symptoms correlate to specific biochemical imbalances.
We compare your cluster
of symptoms to over 20,000 clients who have listed the same group of symptoms
and have also undergone over 100-blood, urine and tissue analysis. Locating the
match of your BioType™ with a subgroup in our database enables us to
extrapolate your unique biochemical profile with 99% surety. In order to
rebalance these underlying biochemical functions, our doctors create an
individualized nutritional program for you.
whfoods.org
Food Advisor Helps You Find
the Foods That Are Right For You: Questionnaire will help analyze your nutritional status
and provide you with information regarding the nutrients, which may be found
deficient in your diet as well as recommendations for which foods and recipes
will help, fulfill your nutritional needs. The Food Advisor can give you a
personalized set of food recommendations from a short questionnaire and move you
along your way to a healthier meal plan!
top
 Vitamin Supplementation
Vitamin Supplementation
Reference -
www.bloodindex.org
Vitamins, used therapeutically, can be of immense help
in fighting disease and speeding recovery. They can be used in two ways,
namely, correcting deficiencies and treating disease in place of drugs. Latest
researches indicate that many vitamins taken in large doses far above the actual
nutritional needs, can have a miraculous healing effect in a wide range of
common complaints and illnesses. Vitamin therapy has a distinct advantage over
drug therapy. While drugs are always toxic and have many undesirable side
effects, vitamins, as a rule are non-toxic and safe.
Reference -
www.ion.ac.uk -
The Institute of Optimum Nutrition
Nutritional
supplements can be enormously beneficial in helping our bodies cope with the
stresses of 21st century life. Sadly not all supplements are the same and in
addition, how you take your supplements can influence their efficacy.
Picking the right supplement takes time and we recommend you seek the advice of
a qualified Nutritional Therapist and visit an independent health food store
where you are likely to get more impartial advice. When you are advised to take
nutritional supplements make sure you fully understand why you are taking them,
how you should take them and what benefit they should offer. Remember that your
supplements are just that - supplements to what should be a healthful, nutrient
dense diet. Taking supplements does not give you license to binge on fast foods
and snacks. They are there to provide that extra intake of nutrients to achieve
optimum levels.
But what are the optimum intakes
of nutrients? What can you achieve from your diet? And what should you consider
supplementing? See our Reference Nutrient Intake values of nutrients and
suggestions for supplementation.
Link
to Vitamin Therapy (in-depth information)
top
Professional & Physician Grade Supplements
Recommend Sources to Purchase Physician Grade Supplements
top
Where
to Buy
Verified Gold Standard Supplements
Link
to Listings of USP Verified Gold Standard Supplements
top
Nutritional Treatment
Applications
Link to
Vitamin Therapy
top
Nutrient Resources
Link
to Vitamin & Mineral Contents of Foods
top
Power Foods
Link
to Listing of Functional (Power) Foods
top
Spiritual Nutrition
He [Jesus] replied, It has been written, Man shall
not live and be upheld and sustained by bread alone, but by every word that
comes forth from the mouth of God. -
Matthew 4:4
Link to Sharing the Word of God, the
Christian Faith
|

|
